|
|
|
|
Emerging Technology: Gateway Courses and Micro-Credentials to Offer
by Jon O'Keefe, Technology Education Jedi
Emerging technology certifications are in demand. The Bureau of Labor Statistics in the United States is predicting a 15% to 20% growth in jobs in the fields of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Data Science (DS) in the next five years. This means more of your customers will be looking to tackle AI and DS projects soon, and you’ll need to be able to provide them with the right training on these topics.
Individuals seeking a career change into a professional AI or DS occupation often find it hard to know where to start, and they lack conceptual understanding of how these emerging technologies are used in business cases. Aside from the shortage of AI specialists and data scientists who are the audience for high-stakes training and certification, organizations also suffer from a lack of understanding in their general workforce of how these technologies will be applied to products and solutions. That lack of conceptual understanding of these technologies will widen the gap between internal teams.

Short theoretical courses or workshops provide delegates with several “aha” moments. These classes cater to management and individuals who need to learn the language of emerging technologies, and to understand how those technologies are commonly used in the business world. In addition to this, these entry level classes act as a gateway for those individuals who are looking to change careers, for example to become machine learning specialists or data ethicists.
Our friends at CertNexus have a compelling portfolio to address this important entry level knowledge. These classes vary in length from 2 hours to a full day and can be taught by instructors who have a strong skillset in the discipline they represent. The following courses are currently available:
-
CyberSAFE – End User Compliance and Awareness Training
-
AIBIZ™ – All about Artificial Intelligence
-
DSBIZ™ – All about Data Science
-
IoTBIZ™ – All about the Internet of Things
-
IRBIZ – All about Incident Response, Security Compliance and Documentation, and setting up a Cybersecurity Team
-
DEBIZ™ - All about the new field of Data Ethics
Special Offer
Logical Operations can help you launch these courses by providing courseware and a certified virtual instructor so you can run one or more of these for your clients. We have currently helped over 30 different training organizations offer 1,000s of students these training courses so that they can return for more advanced certifications. If you are interested in learning more about this, please contact your account manager or email sales@logicaloperations.com.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
What a Fish Dinner Has in Common with Emerging Technologies
by James Varnham, Managing Director, EMEA
|
| |
|
Capturing a customer’s imagination is the ultimate ambition of any salesperson. Whether you are selling pens or courses, you hit the sweet spot when you create an emotion and a desire for the solution that the product will enable.
The acceleration of digital transformation across all industries has disrupted our work, as we all know and are constantly being told. In an incredibly short amount of time, organizations are leveraging the power of data-driven tech to increase employee productivity, improve business performance management, enhance customer experience, increase and optimize process automation, and develop truly innovative products and solutions. However, this also places a burden on organizations to upskill or acquire not only employees with the right technical skills to build these solutions ethically and securely, but also employees who can create the business case, lead the projects, and market and sell the solutions. All these employees need to have a solid understanding of the concepts of the most prevalent emerging technologies—notably, Artificial Intelligence (AI), Data Science (DS), and the Internet of Things (IoT).
This is all well and good, but if you as an Account Executive in a training organization are trying to sell courses on IoT, DS, and AI, there is a fairly high chance that stakeholders at your customers’ organizations are not fully up to speed on these technologies either. “What’s the difference between Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence?” is a question we often get. (For those of you who are reading this who are not technical but have been on an AI Awareness course— I know that will make you chuckle!)
What we all know now when speaking to end customers is that:
-
They collect data.
-
Their data is likely unstructured, and it needs to be cleaned and ethically engineered in order to make it useful.
-
They have great ideas to transform their business if they could develop and implement AI/ML solutions.
However, it can be a challenge to explain how data is collected using IoT devices, what the tasks of a data scientist are, how coding an algorithm works, or what it takes to develop an AI model to use the data. Sometimes you need an analogy and some storytelling if you’re selling to a non-technical person.
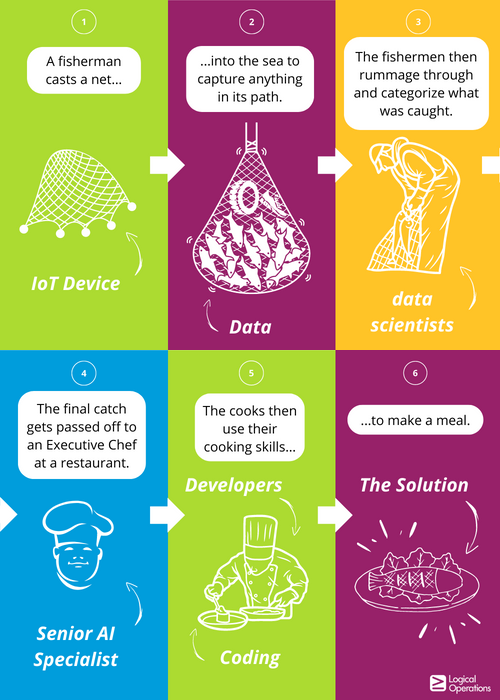
To tie these pieces together, we use the analogy of the process that has gone into the tasty seafood meal that you’re served in a restaurant. What actually happened before this food ended up on your plate? Sounds crazy? Just bear with me.
Imagine a fishing trawler far out at sea. Fishermen cast the net (the IoT device) into the sea in order to capture anything in its path (the data). When they bring the net onboard and empty the contents on the deck, the fishermen (data scientists) have to rummage through and categorize objects (data) in unique piles: fish
over there, car tires in another pile, plastic in another pile, etc.
When they are finished, they go back to shore to pass on their catch to the Executive Chef (Senior AI Specialist) in a restaurant where the cooks (developers) utilize their cooking (coding) skills to make the meal (the solution) ready for customers—without burning or cutting themselves (secure coding).
If you then imagine all the other people and their roles in the restaurant, you can quickly understand the level of knowledge that these people need in order to sell the solution…or in this analogy, make an appetizing meal and leverage an appealing menu to the customers.
Kitchen Staff / Back Office
-
Executive Chef / Senior AI Specialist
- Needs vendor-neutral technical knowledge with multiple specializations in applying a technology to a specific vendor technology.
-
Kitchen manager / Senior Data Scientist / Ethical Emerging Technologist
- Has data scientist qualifications and is ombudsman of corporate ethical framework. Supervises the developers and other data scientists, coordinates work, and ensures that the output is done in an ethical manner.
-
Sous-chef / Machine Learning Specialist and DevOps Engineer
- Needs vendor-neutral technical knowledge. Works closely with the Senior AI Specialist and has an overview of the work of the data scientists and developers. Coordinates with project managers in the front office.
-
Cooks / Developers
- Need coding skills with an emphasis on secure coding practices, in addition to the application of code in the context of building a solution.
Front of House / Front Office
-
Head Waiter, Wait Staff, Bar Staff, Host / VP Sales, Inside Sales, Client Services, Project Managers
- Need AI/DS/IoT awareness-level knowledge and the ability to describe the concept of the technology and the solution.
-
Sommelier / Technical Sales Consultant
- Needs technical knowledge and the ability to describe how the solution was built, what the solution is, and the experience of the solution.
So while this new digital era is daunting in some respects, storytelling and creating analogies can help to enhance understanding and create those “eureka” moments and most importantly, emphasize the importance of training.
What analogies and storytelling do you use when selling to an audience unfamiliar with the process of developing a solution?
|
|
|
|
|
CertNexus Certified Artificial Intelligence (AI) Practitioner (Exam AIP-210): A Sneak Peek
by Jason Nufryk, Instructional Designer
|
| |
|
The next version of the CertNexus Certified Artificial Intelligence (AI) Practitioner (Exam AIP-210) course is currently under development, and I’m excited to give you a preview of how the course has evolved since the initial release of CAIP-110 in 2019.
 Just like the original course, CAIP-210 is driven by a high-stakes, vendor-neutral certification exam. The CAIP-210 exam—due out later this year—was updated to account for various changes in the industry, as well as to align better with the job roles that machine learning practitioners are likely to fill. Just like the original course, CAIP-210 is driven by a high-stakes, vendor-neutral certification exam. The CAIP-210 exam—due out later this year—was updated to account for various changes in the industry, as well as to align better with the job roles that machine learning practitioners are likely to fill.
The new CAIP-210 blueprint condenses the exam domains from six to four, with more emphasis on the overall machine learning workflow: formulating the problem; preparing data and engineering features; training, tuning, and evaluating models; and putting those models into operation. Most CAIP-210 subject matter is not dramatically different from CAIP-110. The new Domain 4.0, however, goes into much more depth on an important aspect of machine learning that the original exam and course covered only briefly: Operationalizing ML Models.
The changes to the exam have brought corresponding changes to the course structure, flow, and content. For example, the course no longer teaches statistical and data visualization concepts, as students are expected to bring this as prerequisite knowledge. Instead, learners will spend more time applying various data preparation techniques, including those for use on unstructured data such as text and audiovisual media.
Like before, the first few lessons in the course set the stage for students to follow a machine learning workflow, whereas the “meat” of the course is all about building many different models from many different algorithms. The algorithms in CAIP-110 appear again in CAIP-210, with the addition of forecasting algorithms as well.
 Instead of ending the course with a lesson about ethics in AI, the ethical risks and strategies for mitigating those risks are sprinkled throughout CAIP-210 within specific contexts. To support exam domain 4.0, the new course concludes with two lessons that let students operationalize their machine learning models by deploying an automated pipeline and integrating it with existing software environments. This MLOps approach is an improvement over CAIP-110, in which students built models in an ad hoc fashion, but didn’t put them into production. Instead of ending the course with a lesson about ethics in AI, the ethical risks and strategies for mitigating those risks are sprinkled throughout CAIP-210 within specific contexts. To support exam domain 4.0, the new course concludes with two lessons that let students operationalize their machine learning models by deploying an automated pipeline and integrating it with existing software environments. This MLOps approach is an improvement over CAIP-110, in which students built models in an ad hoc fashion, but didn’t put them into production.
The course also features general content improvements, including better explanations of certain concepts, a new instructor slide deck, and more robust activities.
For more certification information and a copy of the CAIP-210 exam blueprint, click here. For an early working draft of the CAIP-210 course outline, email assist@logicaloperations.com, or contact your Logical Operations account representative.
I hope this high-level overview has been helpful and that you’re looking forward to the CAIP-210 exam and courseware as much as I am!
|
|
|
________________________________________
|
|
|
Latest Product Highlights
|
| |
|
Reminder: The CertNexus CyberSAFE: Exam CBS-410 eLearning is available!
It includes everything a student needs to be CyberSAFE: eLearning to become more aware of technology-related risks plus the assessment and credential. Shop the CyberSAFE: Exam CBS-410 eLearning now.
|
|
|
|
|
________________________________________
|
|
|
Content Revisions
|
| |
|
Logical Operations revises student and instructor materials based on technical changes, customer feedback, and our own assessment of necessary changes. The revision notes for the most recent updates are below as well as posted on the Content Revisions page. Use this page as a resource to quickly access and view all revision details for any of our recent course updates.
Reminder: When viewing a product on the store, check the Revision Information tab to see the summary description of the most recent revision for that product at any time.
|
|
|
|
|
What is a Vendor-Neutral AI Certification? And Why You Should Add it to Your Instructional Arsenal
by James Varnham, Managing Director, EMEA, Logical Operations and Jeff Felice, President, CertNexus
“Vendor-specific or vendor-neutral”?—a valid question, which is often raised, but the mistake in that statement is the word “or,” which should be replaced with “and.” Here’s why….
 For decades, the question of learning technology either from a vendor-neutral perspective or in the context of a vendor’s technology has persisted. The pre-cloud 2000s was the era of vendor-specific training. Everything was on-premises: servers, networks, databases—you name it. Organizations had fewer choices, and the choices they did have were often hardware dependent, which meant they typically chose a vendor based on the hardware they had or planned to acquire. Of course, there was a percentage of organizations that went down the route of open source and vendor-neutral, citing greater agility in what they needed. But the explosive growth of the Microsofts, IBMs, Ciscos, and Oracles of the world came from getting their technologies humming in almost every company’s data center. For decades, the question of learning technology either from a vendor-neutral perspective or in the context of a vendor’s technology has persisted. The pre-cloud 2000s was the era of vendor-specific training. Everything was on-premises: servers, networks, databases—you name it. Organizations had fewer choices, and the choices they did have were often hardware dependent, which meant they typically chose a vendor based on the hardware they had or planned to acquire. Of course, there was a percentage of organizations that went down the route of open source and vendor-neutral, citing greater agility in what they needed. But the explosive growth of the Microsofts, IBMs, Ciscos, and Oracles of the world came from getting their technologies humming in almost every company’s data center.
Then the cloud came along and disrupted the concept of hosting expensive on-premises data centers. OK, it took a few years of convincing, not least because of security, but trillions of dollars later—we’re here. In fact, you are reading this article from a device connected to a cloud service.
Adoption of the cloud also means that organizations don’t need to have the same level of loyalty to a vendor. Sure, you still need to pick which cloud provider will host your data, but in terms of ancillary technology that you use, and with the emergence of subscription software services, you can, with relative ease and minimal cost, change to something that suits you better— and that includes your cloud services.
What does this have to do with vendor-neutral AI training and certification? Great question…. Keep reading. I’ll start with a couple of analogies.
You’ve just graduated from university with flying colors, and you want to become a brain surgeon. Do you:
-
Look for the best neurosurgery residency.
-
Spend the first 4-6 years learning about the whole body and, once you have graduated as a doctor, specialize in the grey matter.
Or you want to be a commercial airline pilot. Do you:
-
Train on learning to fly a Boeing 777 from the word go.
-
Start with a single-engine crop duster that teaches you the concepts of drag, lift, wind shear, and instrument flight— and THEN, when you get your private pilot’s license that PROVES your “vendor neutral" skills and competencies in flying, apply to an airline that will put you through a 6-month type rating on the Boeing 777, or whichever aircraft they need pilots for.
The same thing applies to technology. Vendor-neutral training helps you understand the general concepts in the field; for example, a solid foundation in machine learning is critical to have before specializing in the development of AI models in Azure, AWS, IBM, Google, etc., environments.
From a trainer’s perspective, if you’re certified to train students in preparation for AI-102T00 (Microsoft Azure AI Engineer), then you will likely not have a problem with the CertNexus Certified AI Practitioner course and certification. Plus, holding this certification will broaden your audience, because you can also teach other students who want to eventually specialize in a multitude of different vendor technologies.
On top of that, we have also seen very innovative solutions that combine CAIP and AI-102T00 into one 7-day event (instead of a 9-day event). Why? Because there is an overlap —you teach the hands-on theory in the 5-day CAIP course, and then cover the specialized application of AI to Azure in the remaining 2 days. Long story short, you don’t leave money on the table, and you provide students with a deeper understanding of AI as well as the application of it to the vendor.
If this has tickled some curiosity, then we would like to invite you to attend a complimentary CertNexus CAIP-210 Train-the-Trainer event from October 24 - 27, 2022 at 10:00 AM - 1:00 PM US Eastern Time. This session will be delivered by PwC Academy’s Senior Manager and expert AI trainer, Semih Kumluk, who draws from his experience in industry and from teaching CAIP to hundreds of delegates around the world in interactive and enjoyable sessions.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
________________________________________
|
|
|
Calling All Instructors: CertNexus CAIP-210 Train the Trainer and Beta Exam Testers Needed
CertNexus CAIP-210 Complimentary Train the Trainer (TTT)
Instructors, mark your calendars! You're invited to attend a complimentary Train the Trainer (TTT) for CAIP-210 delivered by Semi Kumluk, Senior Manager at PwC Academy, Master Instructor, and Certified Artificial Intelligence Practitioner. This TTT event is planned for October 24 -27, 2022 from 10:00 AM - 1:00 PM US Eastern Time. Click here for more details and to register.
CAIP-210 BETA Exam Testers Needed
 CertNexus needs AI/ML professionals (see our list of Common Job Titles) to take the CAIP-210 beta exam and establish the threshold for success. We invite you (or your AI/ML colleagues) to participate in this standard-setting by taking an online proctored exam before October 15, 2022. CertNexus needs AI/ML professionals (see our list of Common Job Titles) to take the CAIP-210 beta exam and establish the threshold for success. We invite you (or your AI/ML colleagues) to participate in this standard-setting by taking an online proctored exam before October 15, 2022.
To participate, please go to the CertNexus Store, create an account (or sign in), and add the exam voucher to your cart. This will provide you with the exam for $49. USERS MUST BE LOGGED IN TO REDEEM THE COUPON. (Note: After the beta period, the exam will retail for $350.)
Upon completion of your order, you will receive a confirmation email. In the coming weeks, it will be followed by a separate email containing the exam voucher and redemption instructions to schedule your exam at Pearson VUE. You will be notified 6-8 weeks after your exam if you passed the exam. If so, you will receive the CAIP-210 badge and certification that is valid for 3 years!
To help you prepare for the AIP-210 exam, you can download the exam blueprint here. For more information on the exam and to view the exam blueprint, which covers all the exam objectives, please visit our website.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Ordering the CertNexus Certified Artificial Intelligence Practitioner Course Materials is Easy
by Chandra Foster, VP, Global Client Services
Get ready to purchase the CertNexus Certified Artificial Intelligence (AI) Practitioner (Exam AIP-210) course later this year!
Follow these easy steps once available:
- Click on the store link https://store.logicaloperations.com/catalogsearch/result/?q=caip
- Utilize the filters on the left NAV to find the mode you want
- Add to your cart
- Log In/Register
- Complete the checkout process

Want more information before you purchase CAIP-210? Contact Client Services for a draft outline to review.
We look forward to supporting you as you prepare for CAIP-210! For the fastest service, email us today at assist@logicaloperations.com.
Chandra Foster
VP, Global Client Services
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|